Delview CSI-Ablinism&DownSyndrome
Down Syndrome
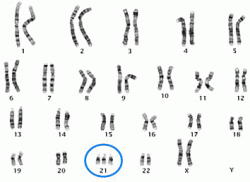
Down Syndrome also known as Trisomy 21 is a condition in which and extra chromosome 21 is added , so instead of having 46 chromosomes in total the person has 47. Down Syndrome is a syndrome that affects your physical and mental development. The physical change is : flat facial profile; upslanting eyes ; flat nasal bridge; a prominent tongue; a single crease along the plams of the hands (transvers palmer) ;smaller limbs ,ears , body and head physical characteristics vary with each person.People with Down Syndrome are often shorter then the average adult person. People with down syndrome also have weaker muscles through out there body, There maybe other medical problems connected with Down Syndrome. There is no way to treat Down Syndrome but there are ways to help speech therapy and physical therapy are often used to help with everyday life for the person with down syndrome
Albinism

Albinism: is the gene mutation of the gene that produces the protein, melanin. Melanin gives your skin, hair and eyes pigment. When the gene is mutated, the person born with albinism will have no or little pigment. To cause this to happen a mutated gene must be passed down from each parent, though “albinos” are usually born to parents of normal pigment. Albinism often occurs along side of vision problems in the eyes caused by undeveloped retinas. Albinism effects 1 in every 17,000 Americans.
Kinds of Albinism:
Kinds of Albinism:
- Ocolocutaneous Albinism I
- Ocolocutaneous Albinism II
- Ocolocutaneous Albinism III
- Ocolocutaneous Albinism IV
- X linked Ocular Albinism
- Hermansky-Pudlak Albinism
- Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
Bibliography
Works Cited
"Albinism: Causes - MayoClinic.com." Mayo Clinic medical information and tools for healthy living - MayoClinic.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 23 Nov. 2009. <http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/albinism/DS00941/DSECTION=causes>.
"Introduction." LunaEterna's Observatory. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Nov. 2009. <http://www.lunaeterna.net/popcult/intro.htm>.
"NOAH — What is Albinism?." NOAH - The National Organization for Albinism and Hypopigmentation. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Nov. 2009. http://www.albinism.org/publications/what_is_albinism.html.
"Down Syndrome - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Diagnosis - Family and Child Health - Body & Health." Site Map - Body & Health. N.p., n.d. Web. 23 Nov. 2009. <http://bodyandhealth.canada.com/channel_condition_info_details.asp?disease_id=44&channel_id=9&relation_id=10860>.
"Down Syndrome ." KidsHealth - the Web's most visited site about children's health. N.p., n.d. Web. 23 Nov. 2009. <http://kidshealth.org/parent/medical/genetic/down_syndrome.html>.
"Down Syndrome-Symptoms." WebMD Children's Health Center - Kids health and safety information for a healthy child. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Nov. 2009. <http://children.webmd.com/tc/down-syndrome-symptoms>.
Leshin, Len, MD, and FAAP. "Trisomy 21: The Origin of DoSyndrome: Health Issues - Medical Essays and Information. N.p., n.d. Web. 23 Nov. 2009. http://www.ds-health.com/trisomy.htm.
"Albinism: Causes - MayoClinic.com." Mayo Clinic medical information and tools for healthy living - MayoClinic.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 23 Nov. 2009. <http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/albinism/DS00941/DSECTION=causes>.
"Introduction." LunaEterna's Observatory. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Nov. 2009. <http://www.lunaeterna.net/popcult/intro.htm>.
"NOAH — What is Albinism?." NOAH - The National Organization for Albinism and Hypopigmentation. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Nov. 2009. http://www.albinism.org/publications/what_is_albinism.html.
"Down Syndrome - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Diagnosis - Family and Child Health - Body & Health." Site Map - Body & Health. N.p., n.d. Web. 23 Nov. 2009. <http://bodyandhealth.canada.com/channel_condition_info_details.asp?disease_id=44&channel_id=9&relation_id=10860>.
"Down Syndrome ." KidsHealth - the Web's most visited site about children's health. N.p., n.d. Web. 23 Nov. 2009. <http://kidshealth.org/parent/medical/genetic/down_syndrome.html>.
"Down Syndrome-Symptoms." WebMD Children's Health Center - Kids health and safety information for a healthy child. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Nov. 2009. <http://children.webmd.com/tc/down-syndrome-symptoms>.
Leshin, Len, MD, and FAAP. "Trisomy 21: The Origin of DoSyndrome: Health Issues - Medical Essays and Information. N.p., n.d. Web. 23 Nov. 2009. http://www.ds-health.com/trisomy.htm.

